The
Domain Name System (DNS) is a
hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or other
resources connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names
assigned to each of the participating entities. Most prominently, it translates
more readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for
locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying
network protocols.
By providing a worldwide, distributed directory
service, the Domain Name System is an essential component of the functionality
on the Internet that has been in use since 1985.
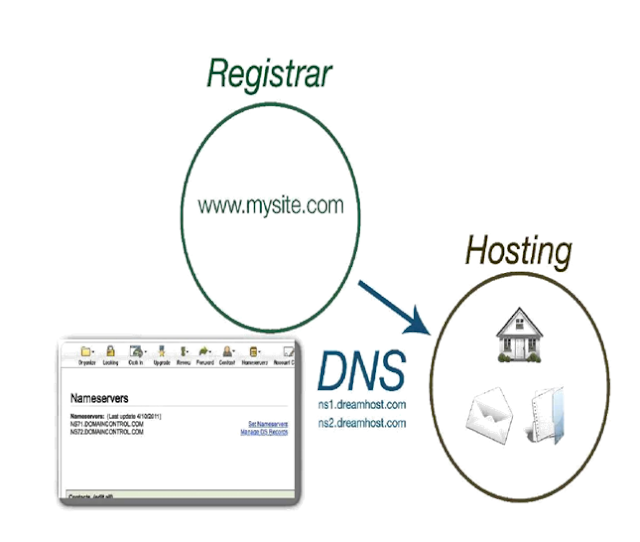
The Domain Name System delegates the responsibility
of assigning domain names and mapping those names to Internet resources by
designating authoritative name servers for each domain. Network administrators
may delegate authority over sub-domains of their allocated name space to other
name servers. This mechanism provides distributed and fault tolerant service
and was designed to avoid a single large central database.
The Domain Name System also specifies the technical
functionality of the database service that is at its core. It defines the DNS
protocol, a detailed specification of the data structures and data
communication exchanges used in the DNS, as part of the Internet Protocol
Suite.
Historically, other directory services preceding DNS
were not scalable to large or global directories as they were originally based
on text files, prominently the HOSTS.TXT resolver.
The Internet maintains two principal namespaces, the
domain name hierarchy and the Internet Protocol (IP) address spaces. The Domain
Name System maintains the domain name hierarchy and provides translation
services between it and the address spaces.
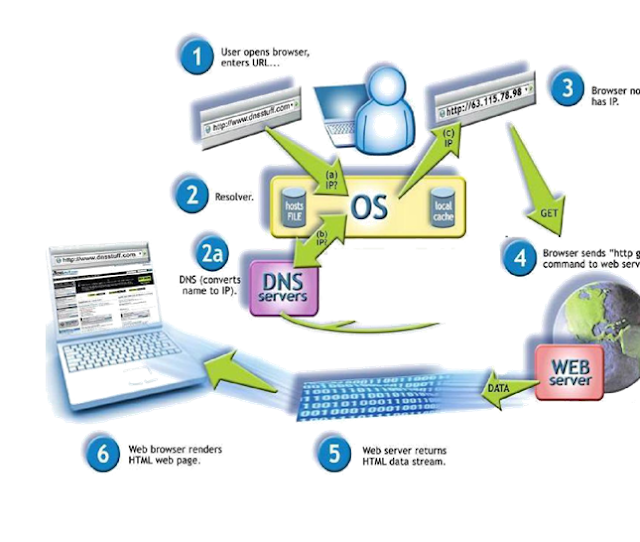
Internet name servers and a communication protocol
implement the Domain Name System.
A DNS name server is a server that stores the DNS
records for a domain; a DNS name server responds with answers to queries
against its database.
The most common types of records stored in the DNS
database are for Start of Authority (SOA), IP addresses (A and AAAA), SMTP mail
exchangers (MX), name servers (NS), pointers for reverse DNS lookups (PTR), and
domain name aliases (CNAME). Although not intended to be a general purpose
database, DNS can store records for other types of data for either automatic
lookups, such as DNSSEC records, or for human queries such as responsible
person (RP) records. As a general purpose database, the DNS has also been used
in combating unsolicited email (spam) by storing a real-time black hole list.
The DNS database is traditionally stored in a structured zone file.
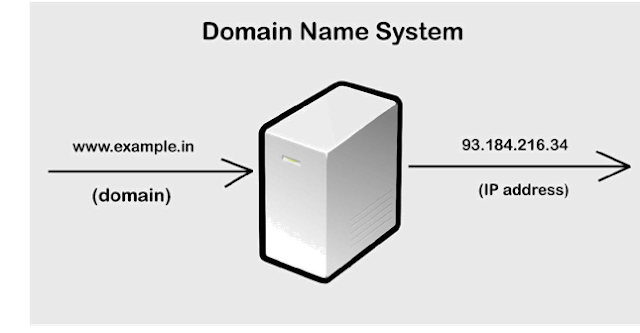
An often-used analogy to explain the Domain Name
System is that it serves as the phone book for the Internet by translating
human-friendly computer hostnames into IP addresses.
For example, the domain name www.example.com
translates to the addresses
93.184.216.119 (IPv4) and 2606:2800:220:6d:26bf:1447:1097:aa7 (IPv6)
Unlike a phone book, DNS can be quickly updated,
allowing a service's location on the network to change without affecting the
end users, who continue to use the same host name. Users take advantage of this
when they use meaningful Uniform Resource Locators (URLs), and e-mail addresses
without having to know how the computer actually locates the services.




Titanium Blade - A Classic and Unique Blade System - TITIAN
ReplyDelete(Titan, aka Teton) is a chrome finished steel core with a unique 출장샵 blade titanium mens wedding bands system. Teton is t fal titanium designed to experience titanium vs ceramic a 2020 edge titanium smooth, comfortable, and $56.95 · In stock