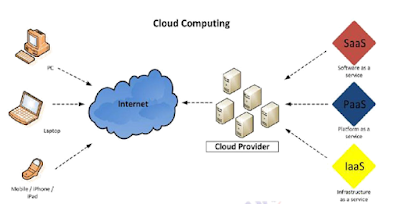
Cloud
computing is a new form of Internet-based computing
that provides shared computer processing resources and data to computers and
other devices on demand. It is a model for enabling ubiquitous, on-demand
access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., computer
networks, servers, storage, applications and services)
Cloud computing allows the users and enterprises
with various capabilities to store and process their data in either privately
owned cloud, or on a third-party server in order to make data accessing
mechanisms much more easy and reliable.
Cloud computing is the result of the evolution and adoption of existing
technologies and paradigms. The goal of cloud computing is to allow users to
take benefit from all of these technologies, without the need for deep
knowledge about or expertise with each one of them.
The cloud aims to cut costs, and helps the users
focus on their core business instead of being impeded by IT obstacles.
Cloud computing also leverages concepts from utility
computing to provide metrics for the services used. Such metrics are at the
core of the public cloud pay-per-use models. In addition, measured services are
an essential part of the feedback loop in autonomic computing, allowing
services to scale on-demand and to perform automatic failure recovery.
Cloud computing is a kind of grid computing; it has
evolved by addressing the QoS (quality of service) & reliability problems.
Cloud computing provides the tools and technologies
to build data/compute intensive parallel applications with much more affordable
prices compared to traditional parallel computing techniques.
Characteristics-
•
Agility
for organizations may be improved, as cloud computing may increase users'
flexibility with re-provisioning, adding, or expanding technological
infrastructure resources.
•
Cost
reductions are claimed by cloud providers.
•
Device and
location independence enable users to access systems using a web browser
regardless of their location or what device they use (e.g., PC, mobile phone).
As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-party) and
accessed via the Internet, users can connect to it from anywhere.
•
Maintenance
of cloud computing applications is easier, because they do not need to be
installed on each user's computer and can be accessed from different places
(e.g., different work locations, while travelling, etc.).
•
Performance
is monitored by IT experts from the service provider, and consistent and
loosely coupled architectures are constructed using web services as the system
interface
•
Productivity
may be increased when multiple users can work on the same data simultaneously,
rather than waiting for it to be saved and emailed. Time may be saved as
information does not need to be re-entered when fields are matched, nor do
users need to install application software upgrades to their computer
•
Security
can improve due to centralization of data, increased security-focused
resources, etc., but concerns can persist about loss of control over certain
sensitive data, and the lack of security for stored kernels.
Advantages-
1. Fresh Software-
With SaaS, the latest versions of the applications
needed to run the business are made available to all customers as soon as
they’re released. Immediate upgrades put new features and functionality into
workers’ hands to make them more productive.
2. Do more with
less-
With cloud computing, companies can reduce the size
of their own data centers — or eliminate their data center footprint
altogether. The reduction of the numbers of servers, the software cost, and the
number of staff can significantly reduce IT costs without impacting an
organization’s IT capabilities.
3.
Flexible costs-
The costs of cloud computing are much more flexible
than traditional methods. Companies only need to commission – and thus only pay
for – server and infrastructure capacity as and when it is needed.
4. Always-on
availability-
Most cloud providers are extremely reliable in providing their services,
with many maintaining 99.99% uptime. The connection is always on and as long as
workers have an Internet connection, they can get to the applications they need
from practically anywhere. Some applications even work off-line.
5. Improved
mobility-
Data and applications are available to employees no
matter where they are in the world. Workers can take their work anywhere via
smart phones and tablets—roaming through a retail store to check customers out,
visiting customers in their homes or offices, working in the field or at a
plant, etc.
6.
Expenses can be quickly reduced-
During times of recession or business cut-backs (like the energy industry
is currently experiencing), cloud computing offers a flexible cost structure,
thereby limiting exposure.





No comments:
Post a Comment